Title: Latest Android Security Features – Enhancing Protection And Privacy
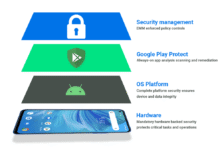
Starting with the latest Android security features, this paragraph aims to engage readers with a brief overview of the topic. The advancements in security measures for Android devices are crucial in safeguarding user data and privacy.
From biometric authentication to app permissions and controls, encryption, security patch updates, malware detection, network security enhancements, and privacy settings, Android continues to evolve to provide a secure digital experience.
Introduction to Android Security Features
Staying up-to-date with the latest security features on Android devices is crucial in today’s digital age where cyber threats are constantly evolving. These security features play a vital role in safeguarding user data and privacy from malicious attacks.
Common Security Threats Addressed by Latest Android Features
The latest Android security features aim to address a variety of common security threats that users may encounter. By implementing advanced security measures, Android devices can better protect against:
- Malware: Android devices are often targeted by malware such as viruses, ransomware, and spyware. The latest security features help detect and remove these malicious programs before they can cause harm.
- Phishing Attacks: Hackers use phishing attacks to steal sensitive information like login credentials and financial data. Android security features help prevent users from falling victim to these scams.
- Unauthorized Access: Protecting devices from unauthorized access is essential to safeguard personal information. Features like biometric authentication and encryption help ensure only authorized users can access the device.
- Data Leaks: Data breaches can result in the exposure of sensitive data to unauthorized parties. Android security features help encrypt data stored on the device and secure communication channels to prevent data leaks.
Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication is a cutting-edge security feature that uses unique physical characteristics to verify a user’s identity. This method offers a higher level of security compared to traditional password-based authentication.
Fingerprint Scanning
Fingerprint scanning is one of the most common biometric authentication methods found on Android devices. It works by capturing and storing a user’s fingerprint data to grant access to the device. This method is known for its speed and accuracy, making it a popular choice among users.
Facial Recognition
Facial recognition technology has made significant advancements in recent years, allowing Android devices to scan and recognize a user’s face to unlock the device. This method is convenient and user-friendly, but concerns regarding its accuracy and security have been raised.
Iris Scanning
Iris scanning is a highly secure biometric authentication method that uses the unique patterns in a person’s iris to verify their identity. While this method offers a high level of security, it is less common on Android devices compared to fingerprint scanning and facial recognition.
Advancements in Biometric Technology
Recent advancements in biometric technology have focused on improving accuracy, speed, and security. This includes the development of multi-modal biometric systems that combine different authentication methods for enhanced security. Additionally, continuous improvements in sensor technology have made biometric authentication more reliable and accessible for users.
App Permissions and Controls
When it comes to managing app permissions, the latest Android security features provide users with a robust system that allows them to control what information and functions apps can access on their devices. This level of control is crucial for ensuring privacy and security.
Specific Controls Over App Permissions
Users have specific controls over app permissions, such as:
- Ability to grant or deny permissions for specific functions like camera, microphone, location, contacts, etc.
- Option to set permissions on a per-app basis, allowing users to customize access levels based on their preferences.
- Revoking permissions that were previously granted to an app if they are no longer needed or trusted.
Significance of Restricting App Permissions
Restricting app permissions is essential for enhanced privacy and security because:
- It helps prevent apps from accessing sensitive data without user consent, reducing the risk of data breaches or misuse.
- Minimizes the exposure of personal information to third-party apps, protecting user privacy.
- Enhances overall device security by limiting the potential attack surface for malicious actors looking to exploit app permissions.
Secure Boot Process
The secure boot process in Android devices plays a crucial role in preventing unauthorized access and ensuring the integrity of the device.
Steps Involved in Secure Boot Process
- Verification of Bootloader: The process begins with verifying the bootloader to ensure it has not been tampered with. This step is essential for establishing a secure foundation for the boot process.
- Authentication of Kernel: Once the bootloader is verified, the next step involves authenticating the kernel to confirm its integrity. Any modifications or unauthorized changes would result in the boot process being halted.
- Validation of OS: After the kernel is authenticated, the operating system (OS) is validated to ensure it has not been compromised. This step helps in maintaining the security of the device at the software level.
- Secure Boot Chain: The secure boot process creates a secure boot chain by verifying each component before allowing the device to fully boot. This chain of trust helps in preventing malware or unauthorized software from running on the device.
Contribution to Overall System Security
The secure boot process significantly contributes to the overall system security by establishing a secure foundation for the device’s boot process. By verifying each crucial component, from the bootloader to the OS, the secure boot process ensures that only trusted and unaltered software can run on the device. This helps in preventing unauthorized access, malware attacks, and other security threats, ultimately enhancing the security posture of the Android device.
Encryption and Data Protection
Encryption plays a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive information on Android devices by converting data into a secure code that can only be accessed with the right decryption key. This ensures that even if a device is lost or stolen, the data remains protected from unauthorized access.
Encryption Methods
- Full Disk Encryption: This method encrypts the entire device storage, including the operating system and user data, providing comprehensive protection against unauthorized access.
- File-Based Encryption: With this approach, each file is encrypted separately, allowing for more granular control over access permissions and providing an added layer of security.
Importance of Encryption
- Protects Sensitive Data: Encryption ensures that sensitive information such as personal documents, passwords, and financial details remain secure, even if the device is compromised.
- Compliance with Regulations: Many industries require data encryption to comply with regulations and protect customer privacy, making it essential for businesses and individuals alike.
Examples of Encryption in Action
- Secure Communication: Encryption is used to secure communications over messaging apps, email services, and browsing activities, preventing eavesdropping and data interception.
- Secure Storage: Encrypted storage ensures that photos, videos, and other files stored on the device remain protected from unauthorized access, maintaining user privacy and confidentiality.
Security Patch Updates
Regular security patch updates play a crucial role in maintaining the security of Android devices by addressing vulnerabilities and strengthening defenses against potential threats.
Significance of Security Patch Updates
- Security patch updates help to fix known vulnerabilities in the Android operating system, ensuring that devices are protected against potential attacks.
- These updates also address bugs and issues that could compromise the security and privacy of user data stored on the device.
- By regularly installing security patches, users can enhance the overall security posture of their Android devices and reduce the risk of falling victim to cyber threats.
Delivery Process and Impact
- Security patches are typically delivered to users through over-the-air (OTA) updates, which are pushed by device manufacturers or mobile carriers.
- These updates are essential for keeping devices secure and up-to-date, as they contain fixes for vulnerabilities identified by security researchers or through the disclosure process.
- Failure to install security patch updates in a timely manner can leave devices exposed to known threats and increase the likelihood of security breaches.
Examples of Addressed Vulnerabilities
-
Stagefright vulnerability:
A critical security flaw in the Android media playback engine that could allow remote code execution through malicious multimedia files.
-
QuadRooter:
A set of four vulnerabilities discovered in Qualcomm chipsets that could potentially compromise the security of millions of Android devices.
-
BlueBorne:
A series of vulnerabilities that enabled attackers to take control of devices via Bluetooth connections, affecting Android devices running older software versions.
Malware Detection and Prevention
Malware detection and prevention are crucial aspects of Android security to protect users’ devices and data from potential threats. By implementing advanced security features, Android devices can effectively identify and remove malware to ensure a secure user experience.
Tools and Techniques for Malware Detection
- Anti-malware software: Android devices come equipped with built-in anti-malware software that scans for and detects malicious software.
- Behavioral analysis: Security features analyze the behavior of apps and files to identify any suspicious activity that may indicate malware presence.
- App sandboxing: Apps run in isolated environments to prevent malware from spreading to other parts of the device.
- Real-time scanning: Continuous monitoring for malware threats in real-time helps to detect and prevent infections promptly.
Importance of Proactive Malware Prevention
Proactive malware prevention measures are essential to safeguard Android devices against evolving threats. By staying ahead of potential malware attacks, users can ensure the security and integrity of their personal information and sensitive data. Implementing regular security updates, avoiding suspicious downloads, and practicing safe browsing habits are crucial in preventing malware infections and maintaining a secure device environment.
Network Security Enhancements
With each new Android update, network security enhancements are introduced to provide users with a more secure online experience. These enhancements are designed to protect users from various network-based security threats.
Enhanced VPN Capabilities
- Android updates now include improved VPN capabilities, allowing users to securely connect to public Wi-Fi networks and protect their data from potential hackers.
- Users can leverage VPN services to encrypt their internet connection and ensure their online activities are kept private and secure.
Network Security Configuration
- Android updates now offer enhanced network security configuration options, allowing users to customize their network settings to meet their security needs.
- Users can set up secure connections, block suspicious networks, and manage their network preferences to enhance their overall security.
Secure Wi-Fi Connection
- Android updates include features that help users identify secure Wi-Fi networks and avoid connecting to potentially risky or unsecured networks.
- Users can benefit from secure Wi-Fi connections to prevent eavesdropping, data interception, and other network-based attacks.
Privacy Settings and Controls
Privacy settings and controls play a crucial role in safeguarding personal information on Android devices. By customizing these settings, users can enhance their overall device security and privacy.
Privacy Settings Customization
- Users can adjust app permissions to control which apps have access to sensitive data such as location, contacts, or camera.
- Privacy settings allow users to manage their biometric authentication preferences, such as fingerprint or facial recognition.
- Users can set up secure lock screen options like PIN, pattern, or password to prevent unauthorized access to their device.
Enhanced Privacy Controls
- Android devices offer the ability to encrypt data stored on the device or SD card to protect against unauthorized access.
- Users can enable two-factor authentication for added security when logging into their Google accounts or accessing sensitive information.
- Privacy controls also include options to restrict background data usage for specific apps to minimize data sharing.
Example of Privacy Control Impact
Adjusting privacy controls can have a significant impact on device security and privacy. For example, by restricting app permissions, users can prevent unnecessary data collection by apps, reducing the risk of data breaches. Similarly, enabling encryption ensures that sensitive information remains protected even if the device is lost or stolen.
Last Point
As we conclude our discussion on the latest Android security features, it’s evident that staying informed and proactive in utilizing these tools is essential for maintaining a secure mobile environment. Embracing these advancements ensures a safer digital experience for users.

is a passionate tech writer and digital lifestyle enthusiast at Tanelly.com. With years of experience covering the latest trends in gadgets, software, gaming, and digital culture, John provides in-depth insights and practical tips to help readers make informed decisions. He combines a love for innovation with clear, engaging writing to deliver content that’s both informative and enjoyable. When he’s not reviewing the newest tech products, John enjoys exploring the intersection of technology and everyday life.